백준 1854번 - K번째 최단경로 찾기
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1854
1854번: K번째 최단경로 찾기
첫째 줄에 n, m, k가 주어진다. (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ m ≤ 2000000, 1 ≤ k ≤ 100) n과 m은 각각 김 조교가 여행을 고려하고 있는 도시들의 개수와, 도시 간에 존재하는 도로의 수이다. 이어지는 m개의 줄에
www.acmicpc.net

해당 문제는 다익스트라 알고리즘을 사용하는 문제이다.
아래의 그림을 보며 이해해보자.
1 노드를 시작해서 4 노드로 가는 방법은 총 3가지 방법이 존재한다.

1) 1-> 4 로 바로 이동하는 방법이 존재한다.
해당 길을 이용하면 distance 는 15가 된다.

2) 1-> 2 -> 4 로 이동 하는 방법이 존재한다.
해당 경로를 이용하면 distance 는 총 4 + 6 = 10 이 된다.

3) 1 -> 3 -> 4 로 이동하는 방법이 존재한다.
해당 경로를 이용하면 distance 는 총 5 + 8 = 13 이 된다.

그럼 위의 세 경로를 distance가 빠른순으로 나열해보면 아래와 같다.
(괄호 안에 있는 숫자는 해당 경로를 사용했을 경우에 distance)
2번 root (10) -> 3번 root (13) -> 1번 root (15)
그럼 문제에서 원하는 K번째 최단경로를 어떤 방식으로 구하면 될지 생각해보자.
예를들어 위 그래프에서 1->4 로 가는 경로중 2번째 최단경로의 distance 를 구하고 싶다고 해보자.
아래와 같이 priority queue 하나를 준비해준다.
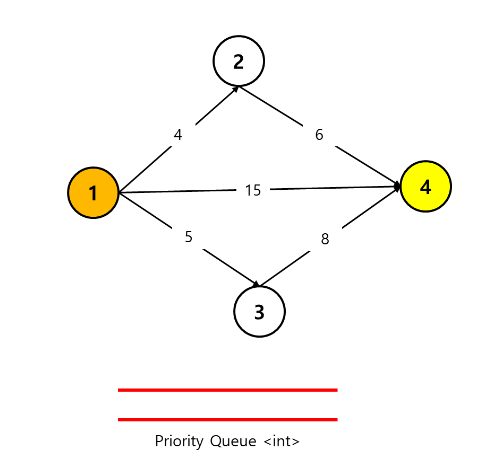
위에서와 같이 첫번째 경로를 살펴보자.
1) 1 -> 4
1 -> 4 로 바로 가는 경로의 distance 는 15이다.
그럼 priority queue 에 아래와 같이 distance 값 15를 넣어줄 수 있다.
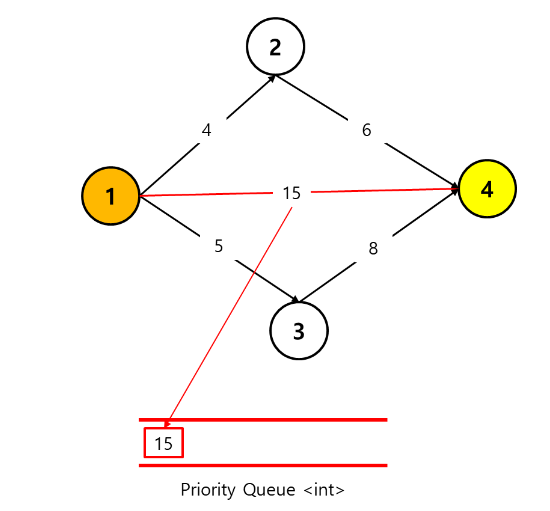
2) 1 -> 2 -> 4
1 -> 2 -> 4 로 가는 경로의 distance 는 4 + 6 = 10 이다.
해당값도 priority queue 에 넣어준다.
queue 의 형식이 priority queue 이므로 정렬을 수반하여 큰 수가 가장 앞쪽으로 오게 강제한다.
그럼 큐의 모습은 아래와 같다.
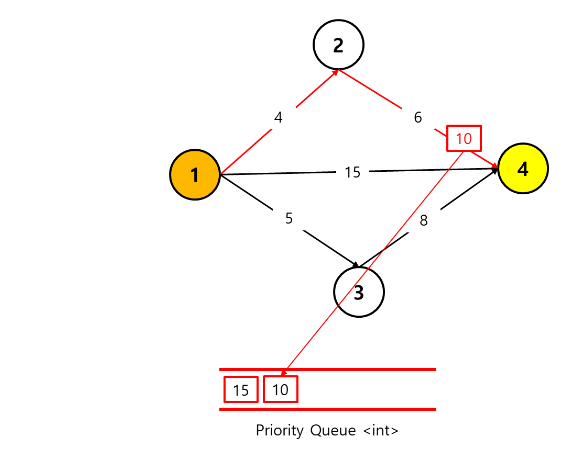
3) 1 -> 3-> 4
1 -> 3-> 4로 가는 경로의 distance 는 5 + 8 = 13 이다.
하지만 우리는 2번째 최단경로를 구하고 싶으므로 priority queue 의 사이즈는 2를 초과해서는 안된다.
그리하여 priority queue 의 가장 선두의 있는 값이 현재 계산된 distance 값보다 큰 경우
priority queue 의 선두 값을 pop 시키고 새로운 값을 넣어준다.
그럼 아래와 같은 큐의 모습이 나오게 된다.
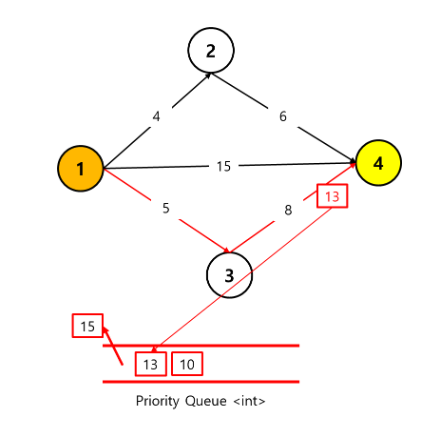
이러한 로직을 사용하게 되면, 그래프 탐색을 마쳤을 경우에 해당 큐에가장 선두의 값이
k번째 최단경로가 된다. 위의 그래프에서 1->4 로가는 2번째 최단경로는 13이 된다.
그럼 위의 로직을 코드로 옮겨보자.
1. C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int N,M,K;
vector< pair<int,int> > map[1002];
priority_queue<int> kth_queue[1002];
void dijkstra() {
priority_queue< pair<int,int> > pq;
pq.push(make_pair(0,1));
kth_queue[1].push(0);
while(!pq.empty()) {
int cur_u = pq.top().second;
int cur_d = -pq.top().first;
pq.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < map[cur_u].size(); i++) {
int next_u = map[cur_u][i].first;
int next_d = map[cur_u][i].second + cur_d;
if (kth_queue[next_u].size() < K) {
kth_queue[next_u].push(next_d);
pq.push(make_pair(-next_d,next_u));
} else if (kth_queue[next_u].top() > next_d) {
kth_queue[next_u].pop();
kth_queue[next_u].push(next_d);
pq.push(make_pair(-next_d,next_u));
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> N >> M >> K;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int u,v,d;
cin >> u >> v >> d;
map[u].push_back(make_pair(v,d));
}
dijkstra();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (kth_queue[i].size() != K) cout << -1 << "\n";
else cout << kth_queue[i].top() << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
2. JAVA
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static class Node implements Comparable<Node> {
int v,d;
public Node(int v, int d) {
this.v = v;
this.d = d;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
if (this.d < o.d) {
return -1;
}
return 1;
}
}
static int N,M,K;
static ArrayList<ArrayList<Node>> map;
static PriorityQueue<Integer>[] resultPq;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer stk = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
N = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
K = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
map = new ArrayList<>();
resultPq = new PriorityQueue[N+1];
for (int i = 0; i <=N; i++) {
map.add(new ArrayList<Node>());
resultPq[i] = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
stk = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
int u = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
int v = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
int d = Integer.parseInt(stk.nextToken());
map.get(u).add(new Node(v,d));
}
dijkstra();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (resultPq[i].size() != K) System.out.println(-1);
else System.out.println(-resultPq[i].peek());
}
}
static void dijkstra() {
PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<Node>();
pq.offer(new Node(1,0));
resultPq[1].offer(0);
while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
int curV = pq.peek().v;
int curD = pq.peek().d;
pq.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < map.get(curV).size(); i++) {
int nextV = map.get(curV).get(i).v;
int nextD = map.get(curV).get(i).d + curD;
if (resultPq[nextV].size() < K) {
resultPq[nextV].offer(-nextD);
pq.offer(new Node(nextV,nextD));
} else if (-resultPq[nextV].peek() > nextD) {
resultPq[nextV].poll();
resultPq[nextV].offer(-nextD);
pq.offer(new Node(nextV,nextD));
}
}
}
}
}